The Polar Vortex: A Chilling Influence on Weather
Introduction – Polar Vortex
The polar vortex, a swirling mass of icy air spinning around Earth’s poles, might seem like a distant phenomenon confined to the Arctic or Antarctic regions. However, its disruptions have far-reaching impacts, shaping weather patterns globally and causing severe cold waves in regions like northern India. This essay explores the polar vortex in detail, its influence on India, and its connection to climate change
Understanding the Polar Vortex
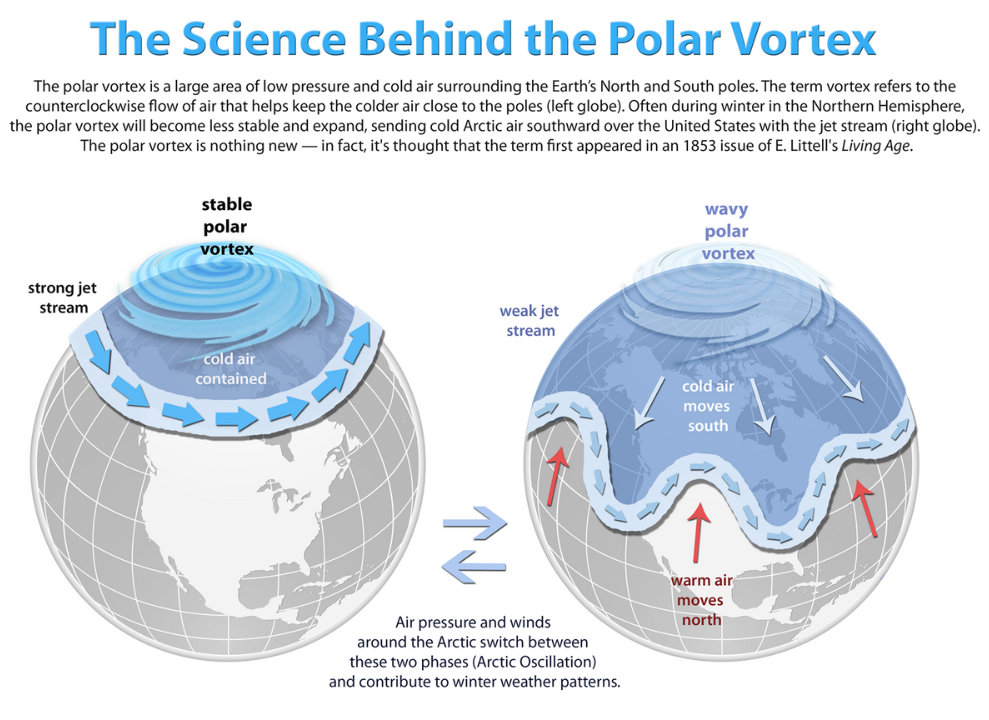
The polar vortex is a vast region of cold, low-pressure air that rotates around the Earth’s poles. It exists in two layers of the atmosphere: the stratosphere (15–50 km above the surface) and the troposphere (up to 15 km, where most weather occurs). This icy, whirling air mass is kept in place by a strong wind current called the jet stream, which flows around it like a boundary fence. Normally, the polar vortex remains stable and contains the cold air within the polar regions. However, when the vortex weakens or splits, it allows freezing Arctic air to escape and travel southwards, influencing weather patterns across continents.
For instance, during its usual behaviour, the polar vortex keeps cold air confined to the poles and warm air to the south. When it destabilises, the jet stream becomes wavy, like a shaken rope. As a result, cold Arctic air escapes into regions far from the poles, including the United States, Europe, and parts of Asia. This causes unexpected drops in temperature, snowstorms, and extreme cold weather events.
How the Polar Vortex Breaks Down
The breakdown of the polar vortex is not random but linked to several atmospheric factors. One major cause is sudden stratospheric warming (SSW), where temperatures in the stratosphere rise rapidly, disturbing the stability of the vortex. Additionally, high-pressure systems can interfere with the polar vortex, pushing it out of its usual circular path and causing parts of it to spill south. These disruptions often result in bitterly cold winters and heavy snowfall in areas unaccustomed to such extremes.
A good example of the polar vortex’s impact is the winter storms in the United States in recent years. During these events, states like Texas, which rarely experience harsh winters, have recorded freezing temperatures and snow. Similarly, Europe and Asia have faced prolonged cold spells, disrupting daily life, agriculture, and transport systems.
The Polar Vortex and India’s Weather
India lies in the tropics and is geographically distant from the polar regions, so it does not experience the polar vortex directly. However, India feels its effects through global atmospheric interactions. When the polar vortex weakens, it disrupts the jet stream and interacts with Western Disturbances, which are crucial for India’s winter weather.
Western Disturbances are storm systems originating in the Mediterranean region. They travel eastward, bringing rain and snow to northern India, especially during the winter months. When Arctic air from a weakened polar vortex meets these systems, the result is often a sharp drop in temperatures, leading to cold waves in states like Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan. These conditions are accompanied by dense fog, frost, and icy winds, making life difficult for millions of people.
Examples of Polar Vortex Impact on India
India has witnessed several instances where the influence of a disrupted polar vortex indirectly caused severe cold waves. For example, in January 2021, northern India experienced unusually cold temperatures, with Delhi recording a minimum of 1.1°C, one of its coldest days in decades. This event was attributed to a weakened Arctic polar vortex, which sent icy air masses southward and intensified Western Disturbances.
Similarly, the December 2019 cold wave saw record-breaking low temperatures across the northern plains. States like Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh shivered under near-freezing conditions, while dense fog paralysed road and rail transport. Experts linked this extreme weather to disturbances in the polar vortex, which affected the global atmospheric circulation.
Another notable instance was the January 2013 cold snap, when Agra recorded a temperature of 0°C, its coldest in 70 years. Again, meteorologists pointed to the weakening of the polar vortex as a factor that enhanced the intensity of Western Disturbances, bringing Arctic air into India.
Why India is Vulnerable to Cold Waves
India’s geography and climate make it particularly susceptible to cold waves triggered by polar vortex disruptions. The Himalayas act as a natural barrier, preventing cold Arctic air from directly sweeping into the subcontinent. However, this does not shield India completely. When the polar vortex weakens, it amplifies the effects of Western Disturbances, which carry the cold air indirectly into the plains of northern India.
Northern India lies at the meeting point of tropical and subtropical climates, making it prone to extreme temperature fluctuations. This is especially evident during winter, when cold air masses from the Arctic interact with the warm, humid air of the Indo-Gangetic plains, resulting in sharp drops in temperature. Additionally, the region’s high population density, lack of proper heating infrastructure, and dependence on agriculture increase its vulnerability to the impacts of cold waves.
The Role of Climate Change
A growing body of scientific research suggests that climate change may be contributing to the instability of the polar vortex. The phenomenon of Arctic amplification, where the Arctic is warming at a faster rate than the rest of the planet, is believed to weaken the polar vortex and the jet stream. As the temperature difference between the poles and the equator decreases, the polar vortex becomes less stable, making it more likely to spill cold air southwards.
While this theory is still debated, some scientists believe that global warming is making polar vortex disruptions more frequent. For instance, Steven Decker, a meteorologist at Rutgers University, explains that warming temperatures in the Arctic reduce the strength of the polar vortex, making it easier for high-pressure systems to destabilise it. However, other experts caution that natural atmospheric variability also plays a role, making it difficult to draw a direct link between climate change and polar vortex behaviour.
Broader Impacts on India
The polar vortex’s influence on India extends beyond cold waves, subtly affecting other critical aspects of the nation’s climate. One key impact lies in winter rainfall patterns, which are primarily driven by Western Disturbances. These systems bring essential rain and snow to northern India, replenishing water resources and aiding agriculture. However, disruptions in the polar vortex can alter the intensity and timing of these disturbances. This can delay much-needed rainfall or, conversely, lead to heavy snowstorms in the Himalayan regions, creating challenges for farmers and communities dependent on consistent weather patterns.
Additionally, the polar vortex can indirectly affect India’s monsoon season, a vital lifeline for the country. Although the monsoon occurs in the summer, changes in global wind circulation caused by a weaker polar vortex can disrupt its onset. For example, delayed or weakened wind patterns can push the rains back, leading to prolonged pre-monsoon heatwaves that stress agriculture and water supplies. These disruptions often challenge farmers and impact crop cycles.
Moreover, interactions between polar vortex disturbances and tropical atmospheric systems can trigger rare extreme weather events. These include hailstorms, unseasonal rainfall, and even heavy snowfall in mountainous regions. Such events not only disrupt daily life but also pose risks to infrastructure, agriculture, and vulnerable populations. Collectively, these impacts highlight the far-reaching influence of this icy Arctic phenomenon on India’s weather and economy.
Mitigating the Effects of Cold Waves
Reducing the impact of polar vortex-induced cold waves in India requires a well-rounded approach combining science, infrastructure, and public policies. Improved weather forecasting is essential, as accurate predictions give farmers and communities the chance to prepare for extreme cold. Advanced meteorological models can alert people to impending cold waves, reducing the risks to crops, infrastructure, and lives.
Agricultural adaptations are also crucial. By developing frost-resistant crop varieties and encouraging crop diversification, farmers can better withstand the challenges posed by harsh winters. These practices help minimise losses, ensuring food security and reducing the economic impact of extreme weather on agriculture-dependent communities.
Investment in better infrastructure is equally important, especially in rural areas. Many vulnerable populations lack proper housing or access to affordable heating. Building insulated homes and ensuring access to cost-effective heating systems can protect people from freezing conditions, reducing cold-related health issues and fatalities.
Finally, public awareness campaigns play a vital role. Educating citizens about cold wave preparedness, such as wearing warm clothing, staying indoors during severe weather, and safeguarding livestock, can save both lives and livelihoods. These efforts create resilient communities equipped to handle the challenges of cold waves, ensuring safety and sustainability in the face of extreme weather. Together, these measures form a comprehensive strategy to mitigate the effects of polar vortex disruptions on India.
Conclusion
The polar vortex, a mighty weather system swirling around the poles, may seem far removed from India’s tropical climate. Yet, its disruptions profoundly affect India, triggering severe cold waves, altering rainfall patterns, and influencing the monsoon. Events like the cold waves of 2021, 2019, and 2013 demonstrate how global atmospheric systems are interconnected and how distant phenomena can shape local weather.
With the growing threat of climate change potentially destabilising the polar vortex further, understanding and adapting to its impacts is more important than ever. By investing in scientific research, improving infrastructure, and promoting sustainable practices, India can build resilience against these extreme weather events and safeguard its people and economy from their chilling effects.
Subscribe to our Youtube Channel for more Valuable Content – TheStudyias
Download the App to Subscribe to our Courses – Thestudyias
The Source’s Authority and Ownership of the Article is Claimed By THE STUDY IAS BY MANIKANT SINGH


