Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana: A Decade of Empowering the Unfunded
PMMY – Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana
Context: Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) which was launched on April 8, 2015, has completed one decade. It aimed to democratise credit by “funding the unfunded” — providing collateral-free loans to micro and small entrepreneurs traditionally outside the ambit of formal finance. A decade on, the scheme has become a cornerstone of financial inclusion, grassroots entrepreneurship, and social equity in India.
Key Achievements Over 10 Years
- Massive Outreach and Disbursal
- Over 520 million loans worth ₹33.65 trillion sanctioned (₹32.87 trillion disbursed).
- About 100 million first-time borrowers, highlighting the scheme’s transformative outreach.
- Loans are disbursed under 4 categories: Shishu (up to ₹50,000), Kishore (₹50,000–₹5 lakh), Tarun (₹5–10 lakh), and Tarun Plus (₹10–20 lakh) introduced in 2024.
- Credit Deepening & Maturity
- Shift from Shishu (92% in 2015) to Kishore and Tarun (now 37%), indicating credit maturation.
- Average ticket size increased from ₹40,000 in FY16 to ₹1.5 lakh in FY25.
- Sanction-to-disbursal efficiency improved: 25.41 lakh crore sanctioned vs 25.32 lakh crore disbursed in FY24.
- Improved Loan Performance
- Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) have declined from 4.77% in FY21 to 3.4% in FY24, showing responsible credit behaviour.
- Gross NPA in FY25 stood at 2.21%, outperforming many other credit segments.
Social Inclusion and Regional Spread
- Women Empowerment
- 68% of loans (₹13.8 trillion across 348 million accounts) and 44% of disbursed amount went to women entrepreneurs.
- Women’s economic empowerment has led to improved household stability and job creation.
- Marginalised Communities
- 50% of beneficiaries are from SC/ST/OBC backgrounds.
- Substantial outreach to minorities (11%) reinforces inclusive growth.
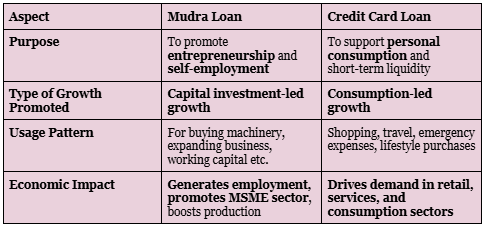
Difference Between Mudra Loan and Credit Card Loan:
State and Regional Trends
- Leading states: Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, West Bengal, Bihar, Maharashtra.
- High per capita account penetration in Tripura (86,320/1L people), Karnataka, and Odisha.
- Expansion even in remote Union Territories like Jammu & Kashmir, reflecting pan-India impact.
Impact on MSMEs and Employment
Human Stories Behind the Numbers
Real-life success stories illustrate PMMY’s transformative capacity:
- Kerala: A woman scaled a mat business 5x via a Shishu loan.
- Punjab: Kishore loan enabled a car service station.
- Tamil Nadu: A daily wage worker became an employer through a floor mill.
These stories embody the scheme’s motto: trusting the smallest dreams.
- MSME credit boom: Lending surged from ₹8.51 lakh crore (FY14) to ₹27.25 lakh crore (FY24).
- PMMY accounts for a significant rise in employment generation—an estimated 25.2 million jobs/year since inception (SKOCH, 2024).
- Shift in mindset: From job-seeking to job-creating, especially in rural and semi-urban areas.
Challenges & The Way Forward
- Strengthening Support Ecosystem: MLIs should provide business advisory, market access, digital skilling, and formal registration assistance.
- Ensuring Scalability: Structured interventions can help enterprises graduate from subsistence to sustainable growth.
- Improved Financial Literacy: Financial and digital literacy must be promoted to avoid misuse and improve repayment quality.
- Better Data Analytics: Real-time performance tracking of loan accounts can enhance targeting and monitoring.
Subscribe to our Youtube Channel for more Valuable Content – TheStudyias
Download the App to Subscribe to our Courses – Thestudyias
The Source’s Authority and Ownership of the Article is Claimed By THE STUDY IAS BY MANIKANT SINGH


