Font size:
Print
Automotive Industry: Powering India’s Participation in Global Value Chains
India’s Automotive Drive into Global Value Chains
Context: NITI Aayog has recently launched the report “Automotive Industry: Powering India’s Participation in Global Value Chains”.
More on News:
- The report highlights India’s strategic vision to transform into a global manufacturing hub in the automotive sector, with a clear roadmap to enhance its participation in the Global Value Chains (GVCs).
- The goal is to increase India’s GVC share from 3% to 8% by 2030, supported by improved manufacturing, R&D, infrastructure, and skill development.
India’s Automotive Landscape:
- Current Position and Potential: Global Automotive Production (2023): ~94 million vehicles; global component market: USD 2 trillion; exports: USD 700 billion.
- India’s Position:
India’s Ambitions by 2030
- Automotive Component Production Target: USD 145 billion.
- Export Target: USD 60 billion, up from current USD 20 billion.
- Trade Surplus: ~USD 25 billion.
- Employment Generation: Additional 2–2.5 million jobs; total direct employment to rise to 3–4 million.
- GVC Share Increase: From 3% to 8%.
- 4th largest automobile producer globally (after China, USA, Japan).
- Production capacity: ~6 million vehicles/year.
- Strong performance in small cars and utility vehicles segments.
- Backed by policies like ‘Make in India’ and a cost-competitive workforce, India is emerging as a critical player in global automotive manufacturing and exports.
Emerging Trends Reshaping the Global Automotive Industry
- Transition to Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- Driven by sustainability concerns, emission norms, and battery tech.
- Boosts demand for lithium and cobalt—reshaping supply chains.
- Rise of Industry 4.0:
- Integration of AI, ML, IoT, Robotics.
- Leads to smart factories, improved flexibility, productivity, and cost-efficiency.
- Promotes new models like connected vehicles and digitised manufacturing.
Challenges in India’s Automotive Sector
- Low Global Component Trade Share: Just ~3% (USD 20 billion) of the global USD 700 billion export market.
- Weakness in High-Precision Segments: Only 2–4% share in engine components, transmission, and steering systems.
- Operational and Structural Constraints:
- High operational costs.
- Infrastructural bottlenecks.
- Low R&D investment (particularly in MSMEs).
- Moderate GVC integration and limited brand recognition globally.
India and the Global Automotive Value Chain (GVC)
The global automotive industry is undergoing a profound transformation driven by shifts in supply chain strategies like China+1 and Europe+1, along with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and increasing geopolitical uncertainties. Amidst this churn, India is emerging as a potential hub in the global automotive value chain (GVC), but significant challenges remain.
Why Global OEMs Are Looking at India
- Geopolitical Realignment: China+1 and Europe+1
- Global OEMs are increasingly diversifying production beyond China due to:
- Rising geopolitical tensions (US-China trade war, Taiwan issue).
- COVID-19 supply chain disruptions.
- Rising labour costs and regulatory scrutiny in China.
- Similarly, the Europe+1 strategy, accelerated by the Russia-Ukraine war, is driving European OEMs to seek cost-effective production bases in stable economies like India.
- Global OEMs are increasingly diversifying production beyond China due to:
- India’s Strategic Strengths
- Large Domestic Market: India is the third-largest automobile market globally by sales.
- Skilled Labor and Engineering Base: Strong talent pool in mechanical and electrical engineering.
- Growing Ecosystem: Presence of global Tier-1 suppliers, expanding R&D centers.
- Policy Push: Schemes like PLI-Auto, FAME-II, and National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) incentivise localisation and innovation.
- EV Potential: Start-ups and conglomerates are investing in battery tech, e-2Ws, and component manufacturing.
- Current Achievements
- Export Growth: India exported over 5 million vehicles in 2022–23, largely two-wheelers and compact cars.
- R&D and Design Centers: Global players like Hyundai, Mercedes-Benz, Bosch, and Continental have R&D operations in India.
- EV Innovations: Tata Motors, Ola Electric, and Ather Energy are spearheading the affordable EV segment.
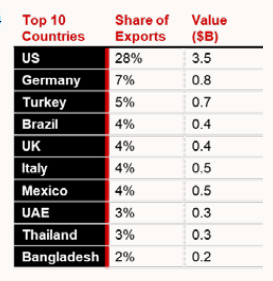
- Auto Components: India is among the top 10 suppliers of auto components globally, exporting to over 160 countries.
Proposed Interventions for GVC Integration
- Fiscal Interventions: Operational Expenditure (Opex) Support: For scaling manufacturing capabilities and Capex (e.g., tooling, dies).
- Skill Development: To create a future-ready workforce and bridge the talent gap.
- R&D and IP Transfer: Incentivising innovation and branding, Facilitating government-enabled IP transfers, especially for MSMEs.
- Cluster Development: Development of common R&D/testing facilities, Promotes collaboration, economies of scale, and supply chain resilience.
- Non-Fiscal Interventions
- Adoption of Industry 4.0:Promoting digital manufacturing and enhanced production standards.
- International Collaboration and FTAs: Encouraging joint ventures (JVs), foreign partnerships, and better market access via FTAs.
- Ease of Doing Business Reforms: Streamlining regulatory processes, Enhancing worker-hour flexibility, supplier discovery, and industrial efficiency.
Way Forward and Conclusion
- India’s automotive sector holds immense potential to become a global manufacturing leader.
- Achieving this requires:
- Center-state coordination.
- Industry participation.
- Focused investment in infrastructure, skills, and R&D.
- With the roadmap outlined in NITI Aayog’s report, India can significantly boost its exports, employment, and GVC share, leading to economic growth and global industrial leadership.



