Font size:
Print
Mouse Brain Mapping
Largest Functional Map of Brain
Context: Scientists have created the largest functional map of a brain to date, identifying and mapping 84,000 neurons in a mouse brain, capturing how these neurons fire and communicate via synapses.
Key Findings
- Mapping the Wiring: Researchers traced the wiring of these neurons across 500 million junctions called synapses, a crucial step toward understanding brain connectivity.
- 3D Brain Reconstruction: The data was assembled into a 3D reconstruction, with different brain circuitry highlighted using various colours, offering an unprecedented view of neural networks.
- Project Significance: This study marks a significant advancement in neuroscience, contributing to understanding the complex networks that enable functions such as thinking, feeling, moving, and perceiving.
- Publicly Accessible Data: The data, published in Nature, is available for scientists and the general public to explore, enabling further research and providing a glimpse into the complexity of the brain.
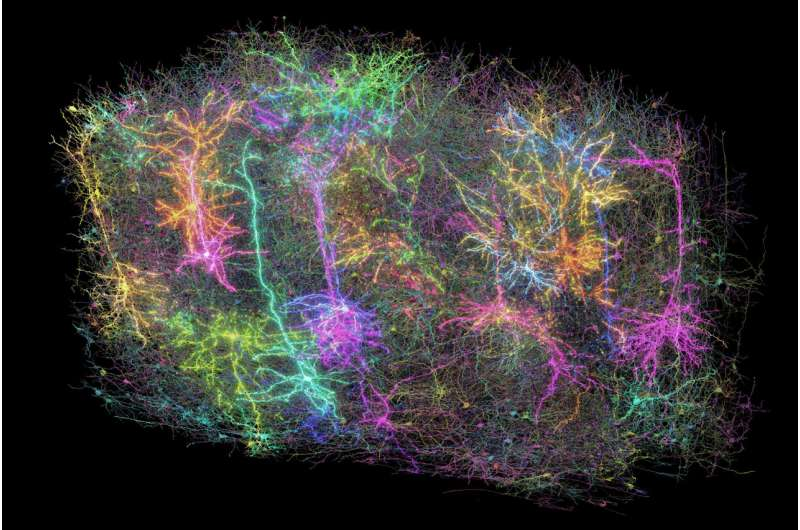
Methodology
- Video Stimulation: Researchers showed the mouse clips of sci-fi movies, sports, animation, and nature. The mouse was genetically engineered to make its neurons glow when activated.
- High-Resolution Imaging: Scientists at the Allen Institute used laser-powered microscopes to capture how neurons in the mouse’s visual cortex activated while processing these videos.
- Electron Microscopy: The tissue was shaved into over 25,000 thin layers. Using electron microscopes, the team captured nearly 100 million high-resolution images to map the neuron connections.
- AI-Assisted Mapping: The data was processed using AI to trace and colour-code individual neural fibres, revealing a detailed map of the neural network.
- Microscopic Wiring: If the neuron wiring were laid out, it would span over 3 miles (5 kilometres).
Applications and Future Impact
- Understanding Neural Networks: The study provides insight into how neurons interact and communicate, potentially offering answers to neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s and autism.
- Path to Brain Disease Treatments: This mapping could help scientists identify abnormal neural patterns linked to brain diseases, providing a foundation for future treatments.
- Comparable to Human Genome Project: Researchers compare this work to the Human Genome Project, suggesting that it could eventually lead to new gene-based treatments for neurological conditions.
- Global Research Collaboration: Over 150 scientists from institutions such as the Allen Institute, Baylor College of Medicine, and Princeton University collaborated on this project, marking a global effort to explore the brain’s complexity.


